
Digitalization and Smart Sensor Technology play an increasingly important role in Industry 4.0. With the advent of both the Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0, new sensors and their related applications are being introduced every day. By combining smart sensors and IoT, Industry 4.0 is conceived as a bridge between the physical and digital worlds. In smart manufacturing facilities, smart sensors provide the opportunity to determine failure, increase efficiency, and monitor levels to design a smart factory. The sensors are vital components of Industry 4.0, allowing several transitions such as changes in positions, lengths, heights, external pressures, and dislocations to be measured, analyzed, and processed.
Sensors are categorized by what is being “sensed” or detected like force, pressure, flow, temperature, proximity, smoke, gas, alcohol, etc. Depending on the type of sensor, its output can be a voltage, current, capacitance, resistance, frequency, or another electrical attribute that varies over time. Here are the 4 types of sensors that enable Industry 4.0
The pressure sensors monitor pipelines and alert supervisors to leaks and inconsistencies that may require maintenance or repairs through a centralized computer system that has real-time tracking. There are countless everyday applications that use these sensors for control and monitoring.
There is also a very common use of temperature sensors in various industrial settings. One of the easiest examples of smart sensors that relate to machines is the use of temperature sensors that connect to a piece of industrial equipment or machinery. This device is connected to an IIoT cloud computing platform and can determine whether a machine or piece of equipment overheats to the point of requiring maintenance or shutting off. Often used in the automobile industry, aviation industry, medical sector, computers, cooking appliances, and other daily applications, these sensors are widely used throughout our everyday lives.
Level sensors provide real-time information to inventory management systems and process control systems about containers, bins, and tanks. There is a wide range of purposes for them, from waste management to irrigation to diesel fuel gauging and many more.
One of the most common applications of a proximity sensor can be in a retail outlet. They can be used in retail outlets to detect customer location and track crowd flow. Different retailers use this technology to ping shoppers’ smartphones with coupon offers they might find on their periphery.
A detailed analysis of smart sensors in nine industries was conducted by EY. According to the analysis, companies across all industrial sectors benefited from the introduction of sensors even with a low degree of implementation. With the highest level of sensor saturation, profit margins (EBITDA) are expected to rise from 11 to 34 percent by 2030 as per EY report.
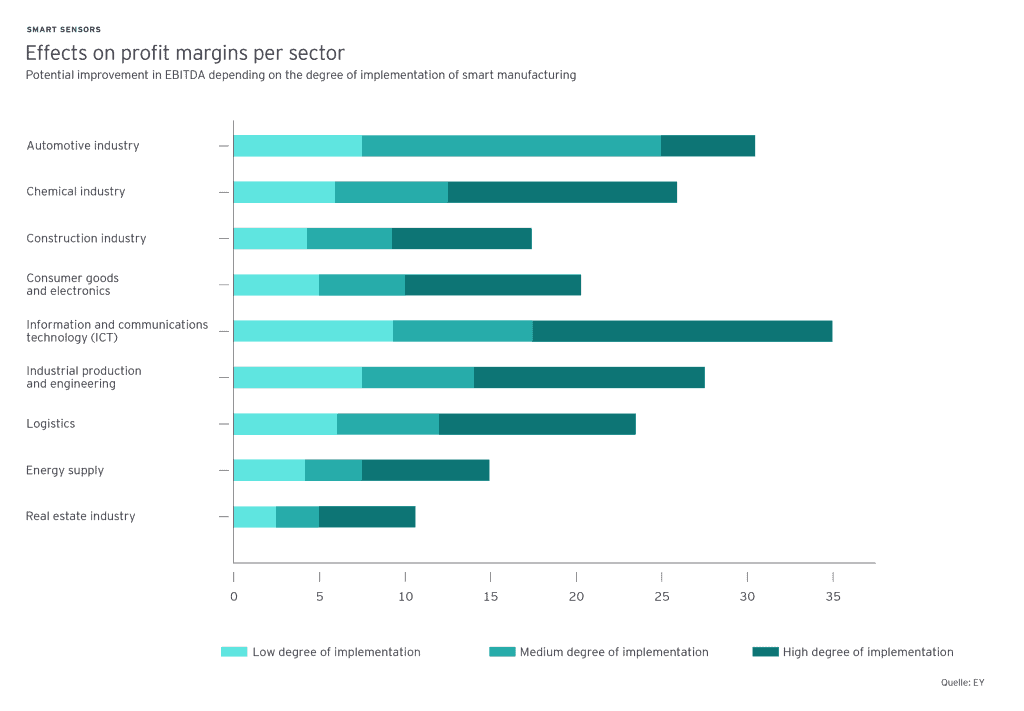
As urbanization and globalization put pressure on primary industries to achieve greater efficiency, there is no doubt that more and more sensors must be smart, connected, and IIoT-ready. Some of the major advantages of smart sensors for Industry 4.0
To get help selecting the right sensors for your application, reach out to our technical support. Click here to contact us.
Thank you for the information. One of our representatives will get in touch with you shortly.